One case of EOB-MRI being useful for diagnosis of mixed-type liver cancer
Tokyo Medical University Hospital
Dr. Kazuhiro Saito, Dept. of Radiology
DATE : 2021
Introduction

Patient’s background
Male; 70s; body weight: 54 kg; mixed-type liver cancer (cHCC-iCC-CLC)
Assessment objectives
Primary complaint: None in particular
History of current condition: A hepatic mass was found during a health check-up, so the patient visited the authors’ hospital for thorough examination. A mass had also been found 1 year previously, and hemangioma was suspected. The mass showed a tendency to expand, so Gadoxetate disodium(Gd-EOB-DTPA) contrast MRI was performed. The alpha-fetoprotein level was slightly elevated, at 10.5 ng/mL.
Previous medical history: Robotic surgery for prostate cancer 5 years previously. Salvage radiotherapy was performed in response to prostate-specific antigen recurrence. Diabetes mellitus.
Contrast agent used
Gadoxetate disodium(Gd-EOB-DTPA) injection, 0.1 mL/kg
Case explanation
Mixed-type liver cancer including cholangiolocellular carcinoma (CLC) was suspected on the basis of factors such as the lesion progression, and laparoscopic partial resection of S4 was performed. In histopathological terms, the central part of the lesion was composed primarily of CLC components, and the circumference was mixed-type liver cancer combining hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and cholangiocellular carcinoma (CC).
Imaging findings

A low-signal lesion 5 cm in diameter was found in the margin of S4 of the liver.
Fig. 1. Simple MRI

Thick, ring-shaped dark staining was found in the arterial phase.
Fig. 2. EOB-MRI arterial phase
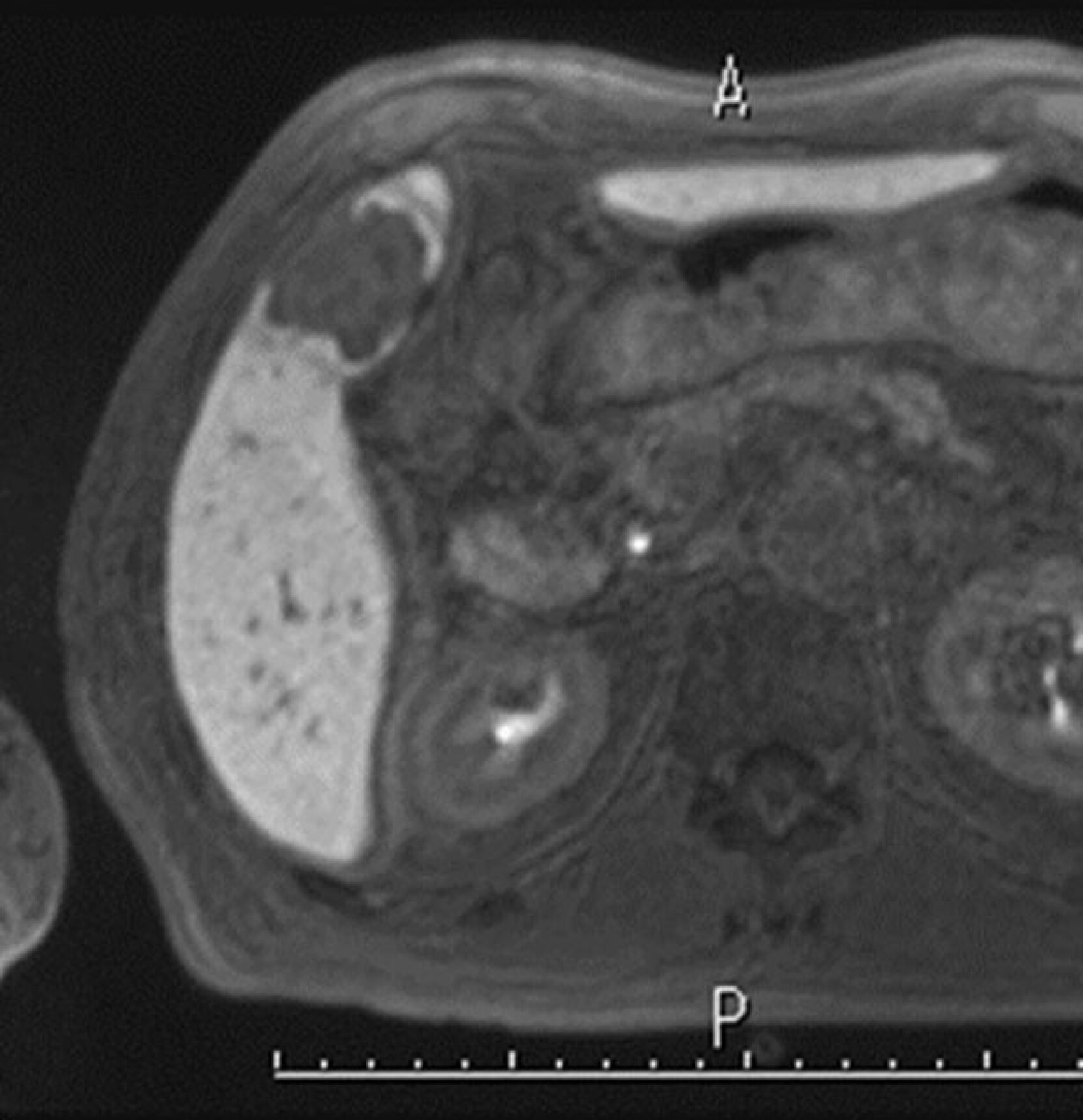
Although most of the mass showed a low signal, a region showing a higher signal than the hepatic parenchyma was found at the margin.
Fig. 3. EOB-MRI hepatobiliary phase

The mass margin showed a high signal, and the central part showed a low signal.
Fig. 4. T2-weighted image

A high signal centered on the margin was found.
Fig. 5. Diffusion-weighted image

A signal slightly higher than the hepatic parenchyma was found.
Fig. 6. ADC map
Photography protocol
| Imaging type | Photography sequence | Photography duration (min:s) | TE (msec) | TR (msec) | FA (deg) | Flipback (yes/no) | Fat sat (type) | ETL (number) |
| Dual echo | 2DFLASH | 2 × 13 s | 2.38/ 4.76 | 125 | 75 | No | DIXON | - |
| Contrast agent administration | ||||||||
| Dynamic | 3D-VIBE | 10s | 1.2 | 3.3 | 15 | No | Q-fat sat | - |
| DWI | SS-EPI | 1:31 | 66 | 5644 | 90 | No | CHESS | - |
| T2WI | 3D-TSE | 5:21 | 149 | 3913 | 120 | No | CHESS | 45 |
| HBP | 3D-VIBE | 20s | 1.2 | 3.3 | 15 | No | Q-fat sat | - |
| Imaging type | P-MRI (Reduction Factor) | Holding breath (yes/no) | NEX (calculation number) | k-space | In-plane resolution (mm) | Slice thickness (mm) | FOV (mm) | Rectangular FOV(%) |
| Dual echo | 2 | Yes | 1 | Linear | 1.3mm×1.3mm | 5 | 400×275 | 68.8% |
| Contrast agent administration | ||||||||
| Dynamic | 2 | Yes | 1 | Linear | 1.3mm×1.3mm | 2 | 400×250 | 62.5% |
| DWI | 2 | No | 4 | Linear | 1.3mm×1.3mm | 5 | 400×320 | 80% |
| T2WI | 2 | No | 1.4 | Linear | 1.3mm×1.3mm | 3 | 400×275 | 68.8% |
| HBP | 2 | Yes | 1 | Linear | 1.3mm×1.3mm | 2 | 400×250 | 62.5% |
| Imaging type | Phase direction (step number) | Read direction (matrix number) | Actual scan (%) | Slice Gap (mm) | Slice number | 3D partition number | 3D actual scan (%) | 3D over sampling(%) |
| Dual echo | 154 | 320 | 70% | 1mm | 30 | ー | ー | ー |
| Contrast agent administration | ||||||||
| Dynamic | 144 | 320 | 72% | 0mm | 96 | 1 | 45% | 0 |
| DWI | 120 | 150 | 62.5% | 1mm | 30 | ー | ー | ー |
| T2WI | 156 | 320 | 71% | 0mm | 64 | 1 | 69% | 12.5% |
| HBP | 150 | 320 | 75% | 0mm | 96 | 1 | 59% | 8.3% |
Devices used and contrast conditions
| MRI device | Avanto 1.5T (Siemens) |
| Automatic injection device | Sonic Shot 50 (Nemoto Kyorindo Co., Ltd.) |
| Workstation | ー |
| Contrast conditions | Dose (mL) | Administration rate (mL/s) | Photography timing | |
| Gadoxetate disodium(Gd-EOB-DTPA) | 5.4 | 2 | Arterial phase: Determined by monitoring scan Portal phase: 70 s after contrast agent administration Transition phase: After 240 s Hepatobiliary contrast phase: After 20 min | |
| Physiological saline solution for flushing | 40 | 2 |
Usefulness of Gadoxetate disodium(Gd-EOB-DTPA) contrast MRI with this patient
With this patient, the existence of a lesion had been demonstrated by abdominal computed tomography 8 years previously. Therefore, a benign lesion such as sclerosing hemangioma was initially suspected. However, as its growth became rapid, consideration was given to treatment, and EOB-MRI was performed. In the arterial phase, ring-shaped dark staining was found, and T2-weighted and diffusion-weighted imaging showed a halo pattern with a high signal in the marginal region, so CC was suspected. In the hepatobiliary phase, on the other hand, a high-signal region was found at the tumor margin, suggesting the existence of hepatocyte-derived components. Due to the presence of HCC components as well as CC components, the diagnosis made was mixed-type liver cancer. Due to the long clinical course, it is probable that it also included CLC components.
As treatment methods for mixed-type liver cancer are different from those for HCC, and it is sometimes not possible to make a correct diagnosis by means of biopsy, preoperative diagnosis is important. With the present patient, the correct diagnosis was made using EOB-MRI.
Precautions relating to administration
9. Precautions relating to patients with specific background factors (taken from the Package Insert)
9.8 Elderly patients
Administration must be performed with care, and with sufficient monitoring of the patient’s condition.
Elderly patients generally have depressed physiological function.
- *The case introduced is just one clinical case, so the results are not the same as for all cases.
- *Please refer to the Package Insert for the effects and indications, dosage and administration method, and warnings, contraindications, and other precautions with use.


