Usefulness of Gadoxetate disodium(Gd-EOB-DTPA) contrast magnetic resonance imaging (EOB-MRI) for judging efficacy after molecular-targeted pharmacotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)
Graduate School of Medicine, Hirosaki University
Drs. Shinya Kakehata, Sho Maruyama, Shingo Kakeda, Dept. of Radiology and Radiation Oncology
DATE : 2021
Introduction

Patient’s background
Female; 70s; body weight: 54 kg; hepatocellular carcinoma; judgment of efficacy of molecular-targeted pharmacotherapy
Assessment objectives
Chronic hepatitis C was first diagnosed at admission to a different hospital for hemorrhagic gastric ulcer. Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and PIVKA-II also increased, and contrast computed tomography (CT) was performed, showing (i) a mass 10 cm in diameter in the right lobe of the liver, which was suspected of being HCC; and (ii) multiple intrahepatic metastases. Therefore, the patient was referred to the authors’ hospital for treatment of the hepatic tumor. As multiple intrahepatic metastases were found in the right lobe of the liver, lenvatinib administration was initiated before surgery.
EOB-MRI was performed to judge the therapeutic efficacy.
Contrast agent used
Gadoxetate disodium(Gd-EOB-DTPA) injection syringe, 0.1 mL/kg
Case explanation
After completing one cycle of lenvatinib administration, in S6 of the liver EOB-MRI showed marked contraction of the mass, and decreased blood flow. Similarly, in S8 of the liver, contraction of the intrahepatic metastases and decreased blood flow were found. Marked decreases in AFP and PIVKA-II levels were also found.
After completing a second cycle of lenvatinib administration, EOB-MRI was again performed to judge the therapeutic efficacy, and it showed that the hepatic S6 lesion had contracted further, but on the other hand the hypervolemic components of the lesion interior and surrounding intrahepatic metastases had increased in size. The PIVKA-II level increased again at the same time. As the condition was considered to be unresponsive to lenvatinib, and the lesion was localized in the right lobe of the liver, extended right lobectomy was performed. In pathological terms, the lesion was moderately differentiated HCC, and a poorly differentiated region was also found. There has been no recurrence during the postoperative time course.
Imaging findings
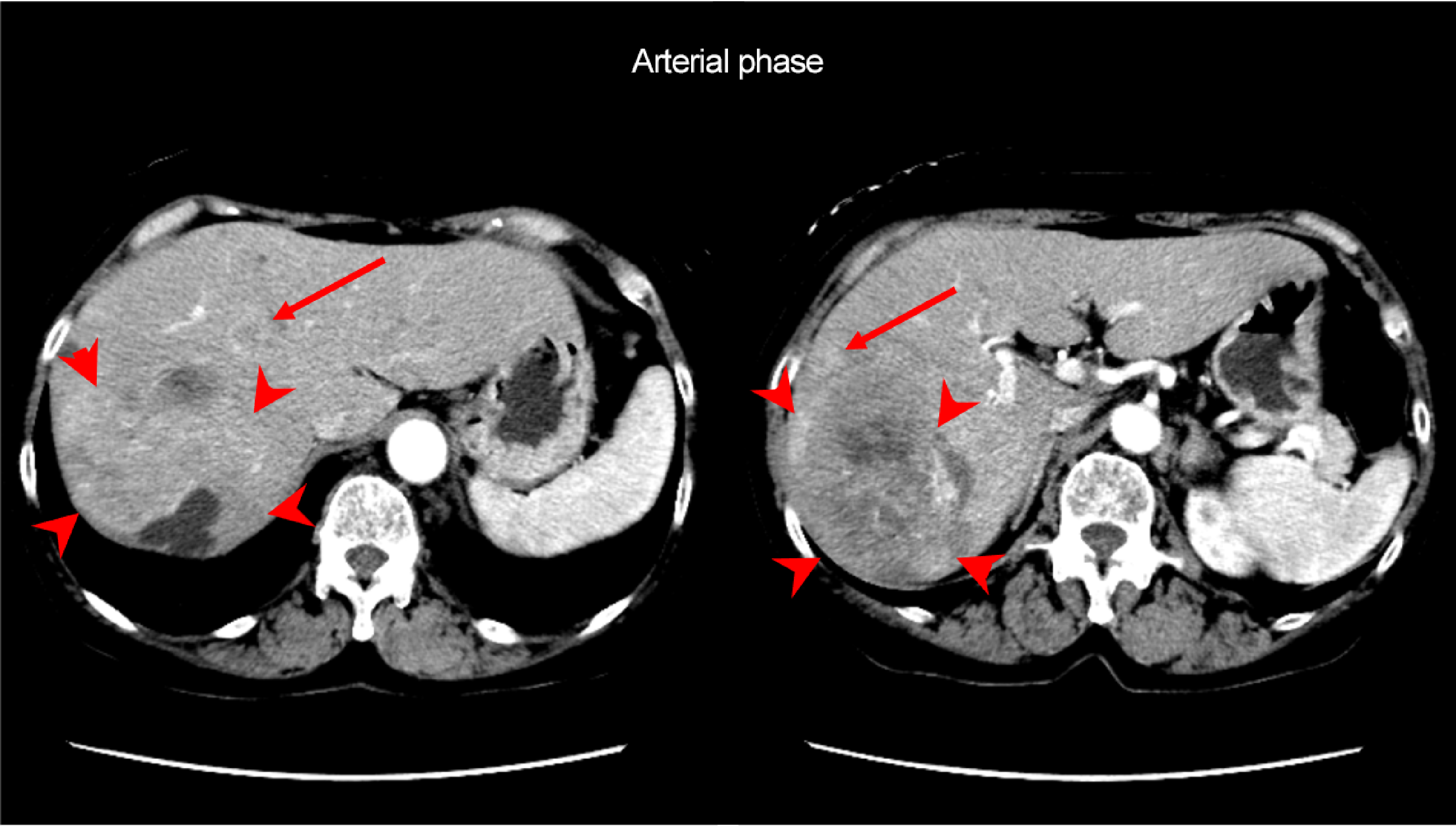

A mass approximately 10 cm in length was found in S6 of the liver (arrowhead), with heterogeneous dark staining in the arterial phase, and low absorption throughout the mass in the equilibrium phase. Moderately or poorly differentiated HCC was suspected. Multiple intrahepatic metastases were found to surround the mass (arrows).
Note: Pretreatment EOB-MRI is not shown, because it was performed at a different hospital
Fig. 1. Dynamic contrast CT arterial and equilibrium phases
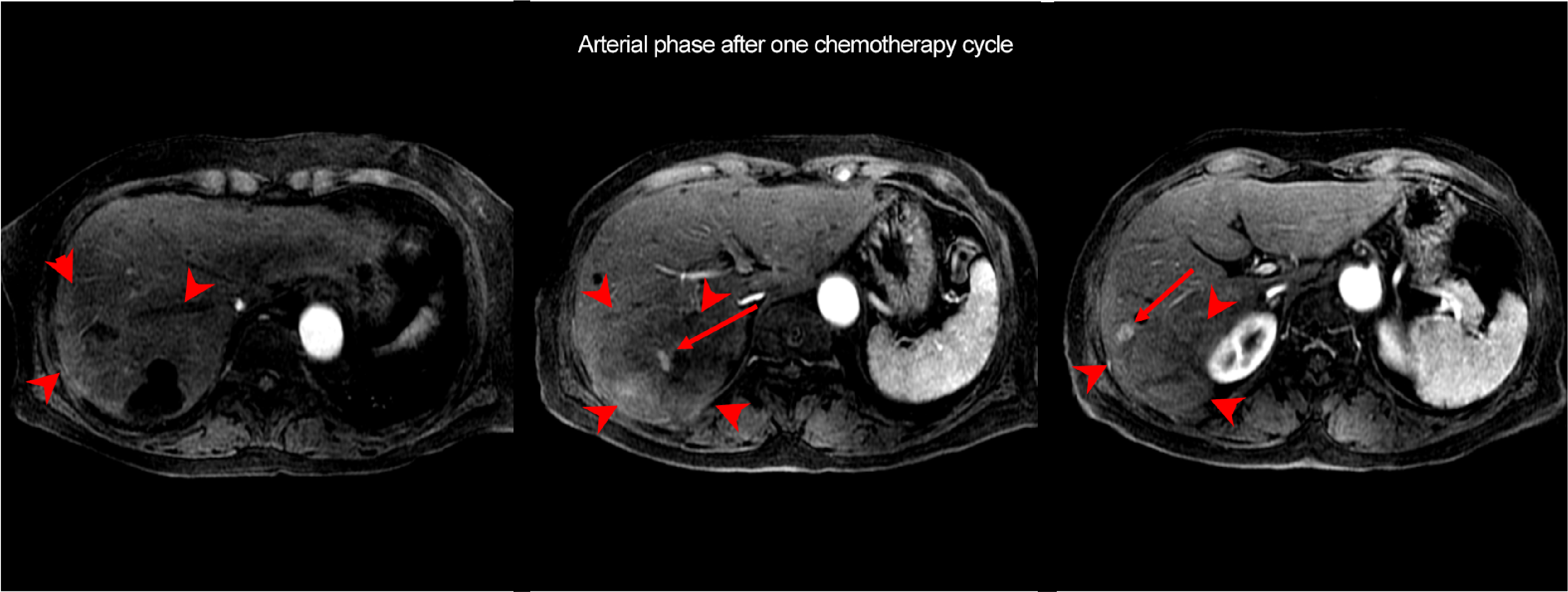
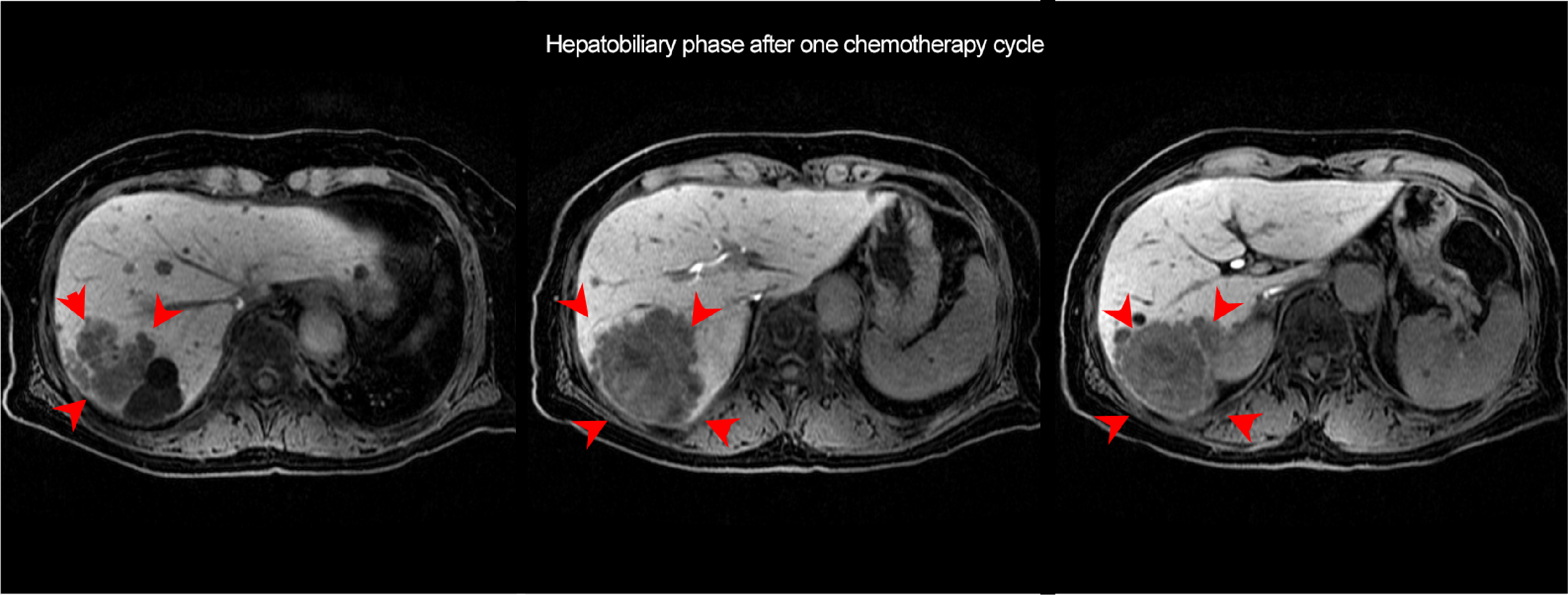
The lesion in S6 of the liver (arrowhead) and the intrahepatic metastatic lesions had contracted, and decreased blood flow was found in the arterial phase. Residual hypervolemic components were found in the interior of the mass (arrow).
Fig. 2. EOB-MRI arterial and hepatobiliary phases after one chemotherapy cycle

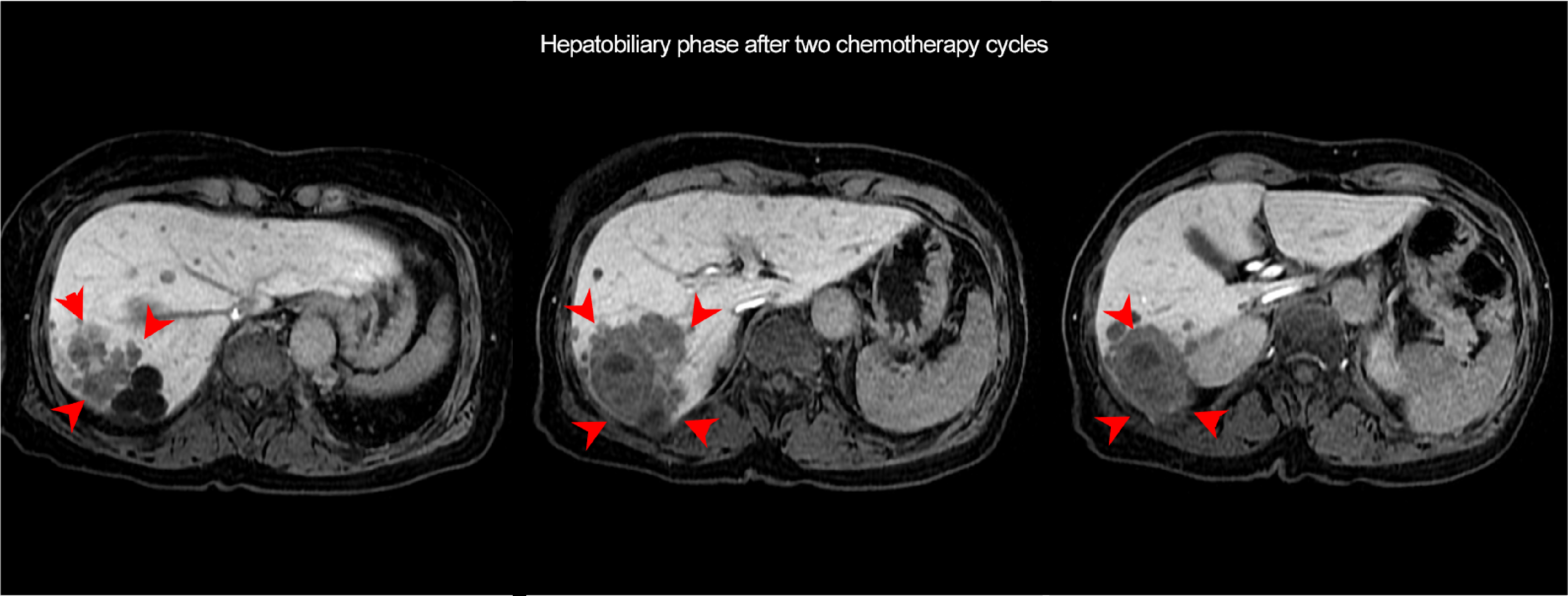
Further contraction of the mass was found in the hepatobiliary phase (arrowheads). Increase in hypervolemic components in the interior of the mass was found in the arterial phase (arrow).
Fig. 3. EOB-MRI arterial and hepatobiliary phases after two chemotherapy cycles
Photography protocol
| Imaging type | Photography sequence | Photography duration (min:s) | TE (msec) | TR (msec) | FA (deg) | Fat sat (type) | ETL (number) | P-MRI (Reduction Factor) | Holding breath (yes/no) |
| Dual echo | FLEX | 0:12 | 1.1/2.4 | 4.3 | 12 | DIXON | ー | ARC 2 | Yes |
| Contrast agent administration | |||||||||
| Dynamic | LAVA | 0:13 | 1.5 | 3.3 | 12 | SPECIAL | ー | ASSET 2 | Yes |
| T2WI | SSFSE | 1:15 | 80 | 2000 | 90 | ー | ー | ASSET 2 | No |
| T2WI | FSE | 2:10 | 85 | 9000 | 90 | CHESS | 18 | ARC 2 | No |
| DWI | EPI | 2:45 | 54.5 | 17000 | 90 | SPECIAL +SSRF | ー | ASSET 2 | No |
| HBP | FLEX | 0:16 | 1.1/2.2 | 4.3 | 12 | DIXON | ー | ARC 2 | Yes |
| Imaging type | NEX (calculation number) | k-space | Slice thickness (mm) | FOV (mm) | Rectangular FOV(%) | Phase direction (step number) | Read direction (matrix number) | Slice Gap (mm) | Slice number |
| Dual echo | 1 | Linear | 4 | 350 | 80 | 192 | 320 | -2 | 92 |
| Contrast agent administration | |||||||||
| Dynamic | 1 | centric | 4 | 350 | 100 | 192 | 320 | -2 | 92 |
| T2WI | 1 | Linear | 6 | 350 | 80 | 256 | 320 | 1.2 | 26 |
| T2WI | 2 | Linear | 6 | 350 | 80 | 192 | 320 | 1.2 | 26 |
| DWI | 3 | Linear | 6 | 400 | 100 | 80 | 80 | 1.2 | 26 |
| HBP | 1 | Linear | 3 | 350 | 80 | 192 | 320 | -1.5 | 124 |
Devices used and contrast conditions
| MRI device | Signa HDxt 3T |
| Automatic injection device | Solaris |
| Workstation | ー |
| Contrast conditions | Dose (mL) | Administration rate (mL/s) | Photography timing | |
| Gadoxetate disodium(Gd-EOB-DTPA) | 5.3 | 1 | Imaging at initiation of breath-holding, on reaching the abdominal aorta, using Smart prep | |
| Physiological saline solution for flushing | 20 | 1 |
T2WI/DWI was used together with respiratory synchronization.
Usefulness of Gadoxetate disodium(Gd-EOB-DTPA) contrast MRI with this patient
The therapeutic efficacy of molecular-targeted drugs for HCC was judged in accordance with the m-RECIST and/or RECICL criteria, taking into consideration not only tumor contraction, but also elimination of tumor dark staining. With the present patient, although the tendency toward tumor contraction was maintained, the PIVKA-II level increased again, and increased blood flow in the tumor was found in the Gadoxetate disodium (Gd-EOB-DTPA) contrast MRI arterial phase. In addition, evaluation of multiple intrahepatic metastases, and evaluation of the presence or absence of new lesions both in the hepatobiliary phase and by diffusion-weighted imaging, offer the major advantage of enabling sensitive detection even in a state of reduced tumor blood flow due to treatment with a molecular-targeted drug.
Precautions relating to administration
9. Precautions relating to patients with specific background factors (taken from the Package Insert)
9.8 Elderly patients
Administration must be performed with care, and with sufficient monitoring of the patient’s condition.
Elderly patients generally have depressed physiological function.
- *The case introduced is just one clinical case, so the results are not the same as for all cases.
- *Please refer to the Package Insert for the effects and indications, dosage and administration method, and warnings, contraindications, and other precautions with use.


