Usefulness of EOB-MRI in the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma and adenoma in the same patient.
National Taiwan University Hospital and College of Medicine
Chih-Horng Wu, National Taiwan University Hospital, Department of Medical Imaging
Hung-Chih Yang, National Taiwan University College of Medicine
DATE : 2022
Patient characteristics

Patient’s background
41 years old male, 70kg
Disease: Hepatocellular carcinoma and adenoma in the same patient
Investigation objectives
The patient was a HBV carrier and visited the hospital with asymptomatic liver tumors noted by ultrasound during surveillance. Dynamic CT showed a hypervascular tumor at S8, a hypovascular lesion at S6 and multiple small hypervascular stains at peripheral portion. Due to different enhancing pattern of the S8 and S6 lesions, EOB-MRI was arranged for further investigation.
Contrast agent used
Gadoxetate disodium(Gd-EOB-DTPA) injection 0.1 mL/kg
Case description
The EOB-MRI showed a hepatic tumor at peripheral S8 with high signal intensity on T2WI and low signal intensity on T1WI. The dynamic study showed global enhancement in the arterial phase, washout in the portal venous phase and low signal intensity in the hepatobiliary phase, indicating typical HCC. Furthermore, a hepatic tumor at peripheral S6 with high signal intensity on T2WI, signal drop in opp-phase compared with in-phase, faint enhancement in the arterial phase and low signal intensity in the hepatobiliary phase, indicating fat-containing tumor. Therefore, the preoperative diagnosis of the S8 lesion was typical HCC and the S6 lesion was hepatic adenoma, angiomyolipoma or HCC with fat metamorphosis. The patients received right lobectomy and the pathologic results showed HCC at S8 and hepatocellular adenoma at S6.
Images
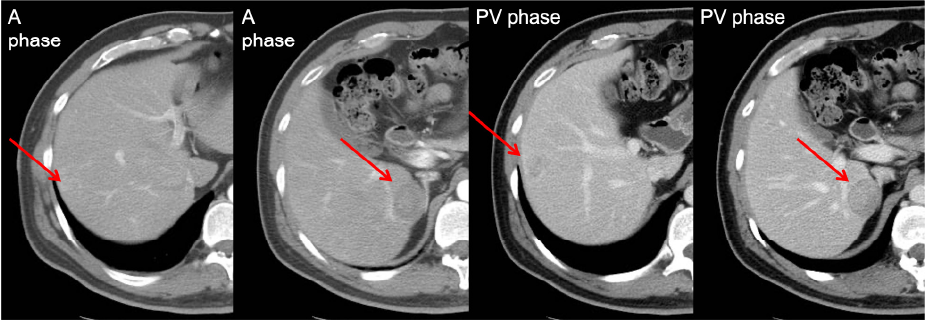
A hypervascular tumor at S8, a hypovascular lesion at S6
Figure 1. Two hepatic lesions in dynamic CT
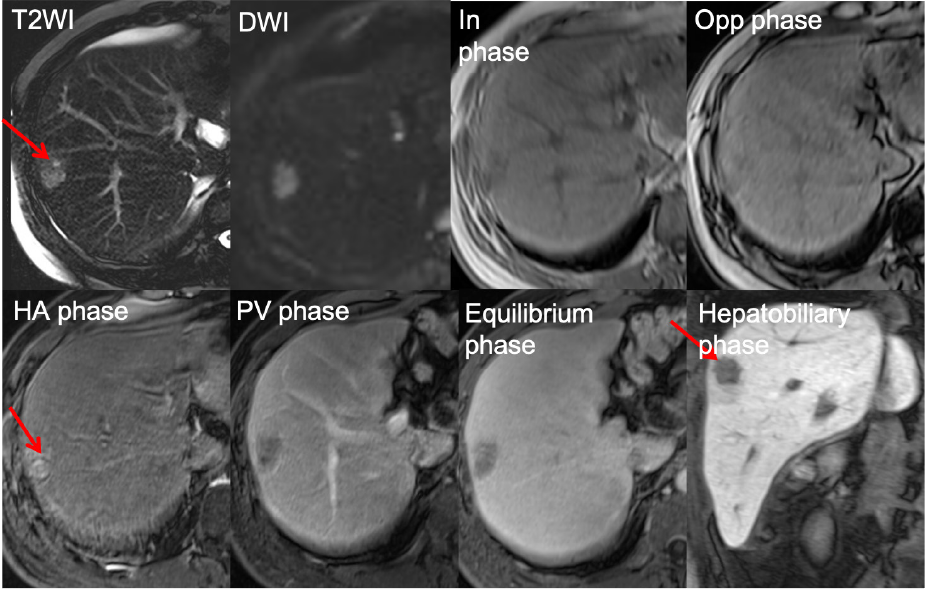
High signal intensity on T2WI and low signal intensity on T1WI. Typical dynamic enhancing pattern, indicating HCC.
Figure 2. EOB-MRI for the S8 lesion
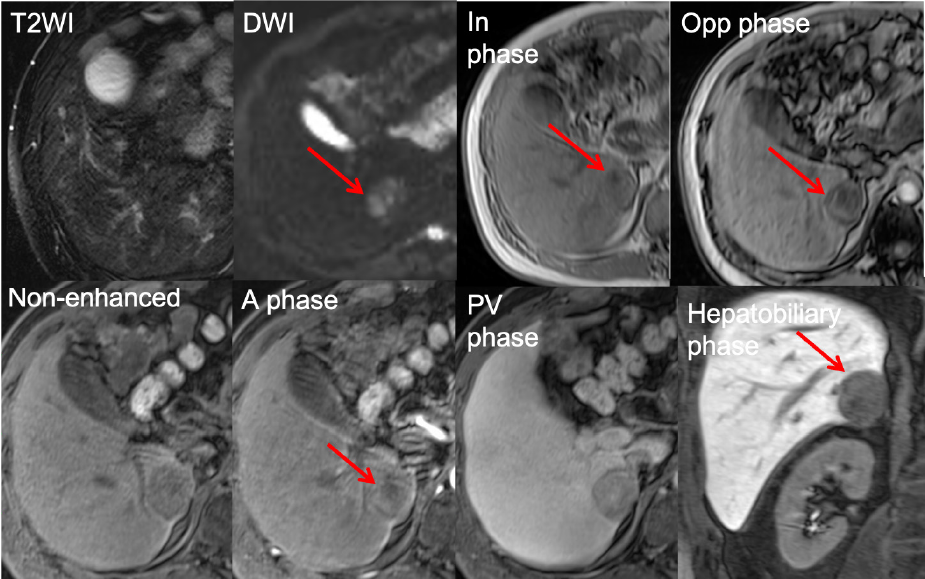
Signal drop in opp-phase and faint contrast enhancement
Figure 3. EOB-MRI for S6 lesion
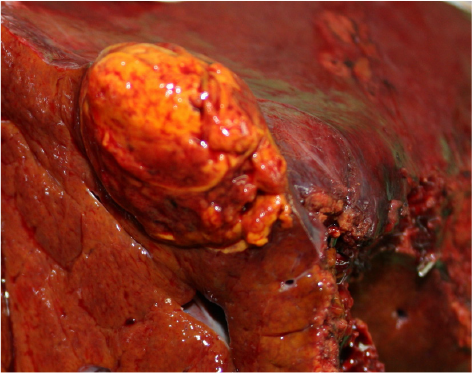
Tumor 1 (Segment 6): Hepatocellular adenoma
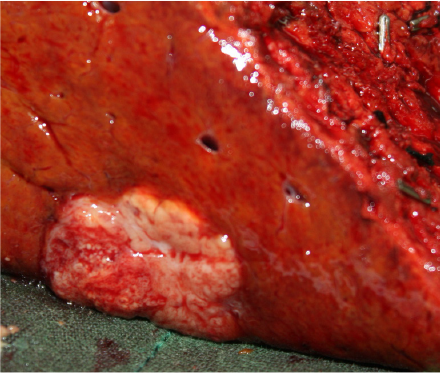
Tumor 2 (Segment 8): Hepatocellular carcinoma
Figure 4. Operation findings and Pathologic report
Usefulness of contrast-enhanced MRI with Gadoxetate disodium(Gd-EOB-DTPA) in this case
The S8 tumor had typical imaging pattern for HCC but the S6 tumor has fat-containing component. Therefore, hepatocellular adenoma or angiomyolipoma was considered first but HCC with fat metamorphosis cannot be excluded. Furthermore, the S6 tumor is faint enhancement in arterial phase, so hepatocellular adenoma is more favored. However, the patient is young and the liver function is good. For sufficient safety margin and complete tumor resection, we chose right lobectomy for this patient.
Imaging protocol
Devices used and contrast conditions
| MRI device | Siemens Magnetom Verio 3T system |
|---|---|
| Automatic injection device | Yes |
| Work station | syngo MR B19 |
| Contrast conditions | Dose (mL) | Administration rate (mL/s) | Photography timing | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gadoxetate disodium(Gd-EOB-DTPA) | 10 | 1 | Bolus tracking | |
| Physiological saline solution for flushing | 20 | 2 |
| Imaging type | Photography sequence | Imaging duration | TE (msec) |
TR (msec) |
FA (deg) |
Breath hold (Present/Abs ent) |
In-plane resolution (mm) |
Slice thickness (mm) |
Slice gap (mm) |
Number of slices |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dual echo | T1_vibe_opp-in | 11 sec | 1.38/2.48 | 4.4 | 9 | present | 2.5 | 2.5 | 0 | 88 |
| Contrast agent administration | ||||||||||
| Dynamic | Vibe | 14 sec | 1.15 | 3.27 | 15 | present | 1.9 | 1.9 | 0 | 128 |
| DWI | b=0,600,1000 | 3 mins | 82.1 | 20,000 | 90 | absent | ー | 5 | 1 | 50 |
| T2WI | Ax T2 FS | 1 min | 74 | 2600 | 123 | present | ー | 5 | 1 | 40 |
| HBP | Vibe | 14 sec | 1.15 | 3.27 | 15 | present | 1.9 | 1.9 | 0 | 128 |
- *The case introduced is just one clinical case, so the results are not the same as for all cases.
- *Please refer to the Package Insert for the effects and indications, dosage and administration method, and warnings, contraindications, and other precautions with use.


