Usefulness of EOB-MRI in the diagnosis of combined hepatocellular carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma
National Taiwan University Hospital and College of Medicine
Chih-Horng Wu; National Taiwan University Hospital
Hung-Chih Yang, National Taiwan University College of Medicine
Contrast agent used/Dose
Gadoxetate disodium(Gd-EOB-DTPA) injection 0.1 mL/kg, 10mL
Patient characteristics
Age/Sex/Weight
78 years old female, 46kg
Patient characteristics and purpose of contrast-enhanced MRI
The patient had cryptogenic (non-HBV and non-HCV) liver cirrhosis and visited the hospital with an asymptomatic liver tumor noted by ultrasound during surveillance. She also had type 2 diabetes mellitus and breast low-grade ductal adenocarcinoma in situ, right, s/p needle localized partial mastectomy, breast-conserving therapy, and axillary lymph node dissection 9 years ago. The US showed a hypoechoic lesion at S8 with hepatic steatosis. CT also demonstrated a tumor at S8 with arterial heterogeneous enhancement in the arterial phase but no definite portal venous washout. Therefore, she received EOB-MRI to clarify the nature of the tumor.
Disease(s)
Combined hepatocellular carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma
Case description
The EOB-MRI showed cirrhotic pattern with uneven hepatic surface, coarse hepatic architecture and signal drop in out phase image, indicating fatty liver. A hepatic tumor at peripheral S8 with high signal intensity on T2WI and low signal intensity on T1WI. The dynamic study showed global enhancement in early arterial phase and peripheral enhancement in late arterial phase. Furthermore, there was also different signal intensity at the central and peripheral portions of the tumor. The laboratory data were total/direct bilirubin: 2.07/0.41 mg/dL, AST/ALT: 82/58 U/L and tumor markers were AFP: 8.01 ng/mL and CA 19-9: 23.3 U/mL. Therefore, combined hepatocellular carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma was impressed. The patients received right atypical hepatectomy and the pathologic results showed combine hepatocellular and cholangiocarcinoma: 50% and 50%.
Images
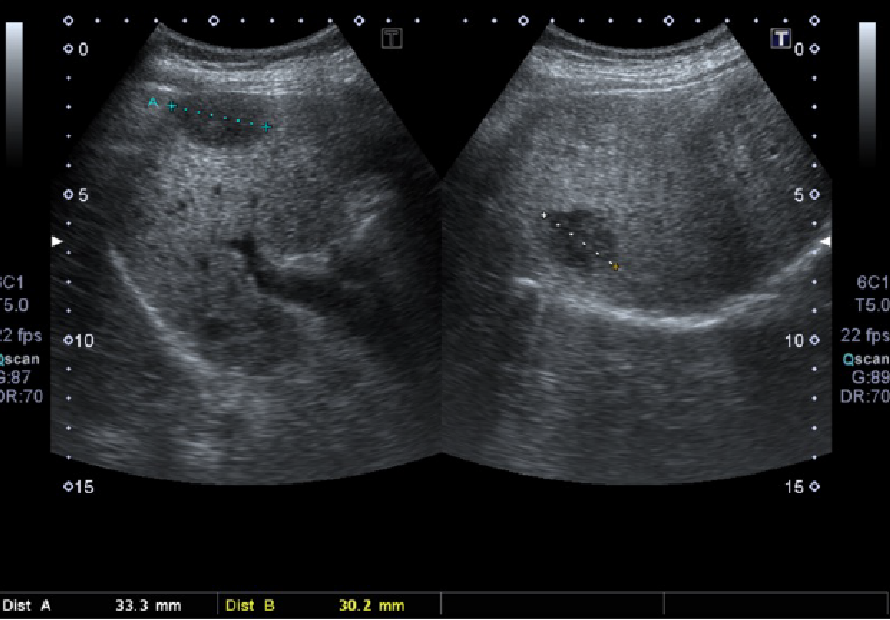
Figure 1. Ultrasound image
A hypoechoic lesion at subcapsular region
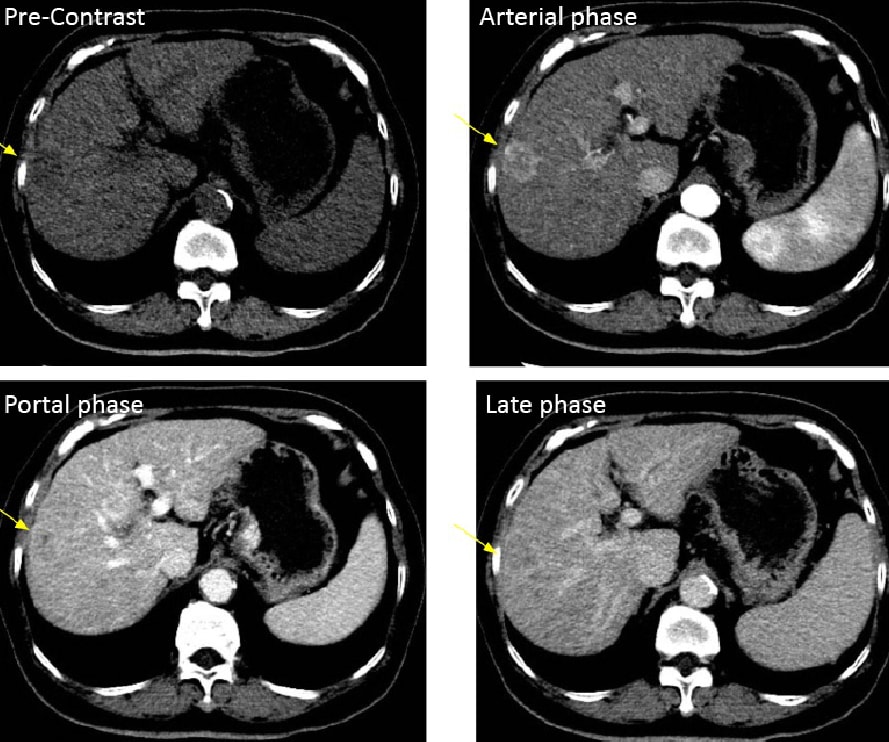
Figure 2. Dynamic CT
CT showed a hepatic tumor at peripheral S8 (yellow arrow).
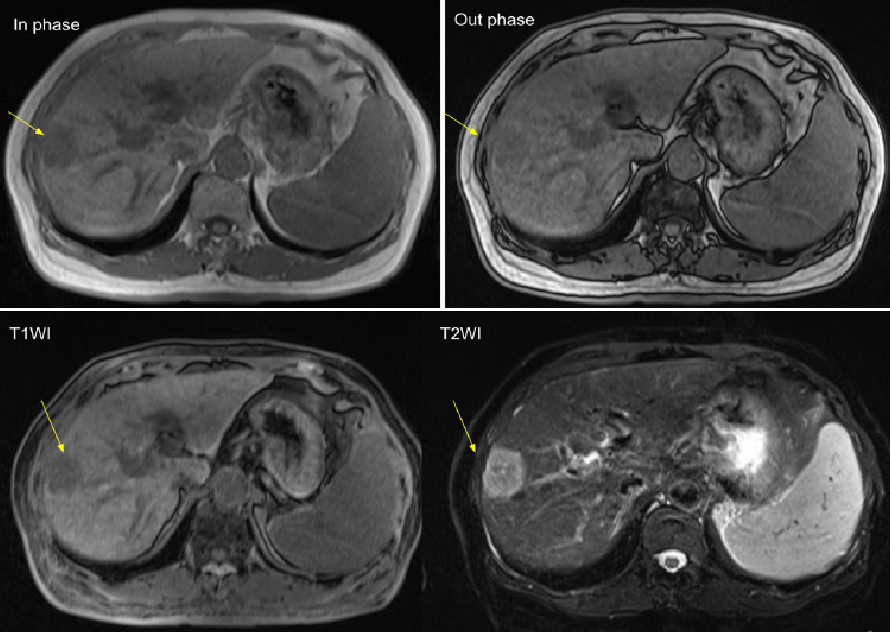
Figure 3. EOB-MRI (T1 and T2)
The tumor at S8 showed high on T2 and low on T1 (yellow arrow).
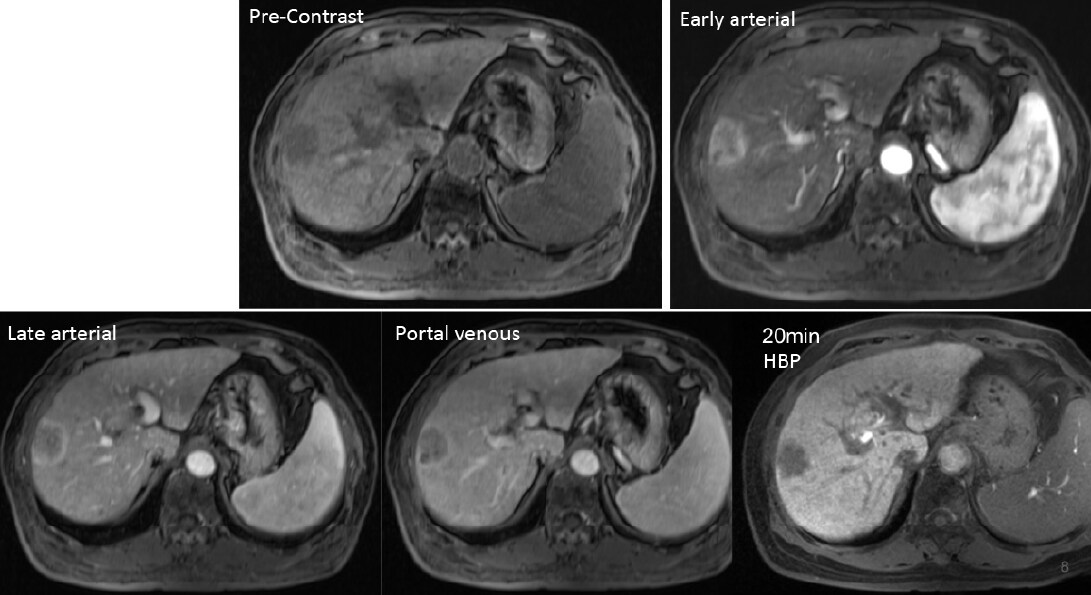
Figure 4. EOB-MRI (dynamic)
The S8 lesion had different pattern between early and late arterial phases
Usefulness of contrast-enhanced MRI with Gadoxetate disodium(Gd-EOB-DTPA) in this case
Right atypical hepatectomy was performed after EOB-MRI under the suspicious of combined hepatocellular carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma. The hepatocellular carcinoma usually had global arterial enhancement and the cholangiocarcinoma usually had peripheral arterial enhancement. This case had both imaging characters in early and late arterial phase and two different signal intensity and peripheral and central portions in hepatobiliary phase. Therefore, it was reasonable to suggest combined hepatocellular carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma.
Photography protocol
Devices used
| MR device used | Siemens Magnetom Verio 3T system |
|---|---|
| Autoinjector | Yes |
| Workstation | syngo MR B19 |
| Contrast enhancement condition |
Dose (mL) | Infusion rate (mL/sec) |
Imaging timing | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gadoxetate disodium(Gd-EOB-DTPA) | 10 | 1 | Bolus tracking | |
| Physiological saline chaser | 20 | 2 |
| Imaging type | Imaging sequence | Imaging duration |
TE (msec) |
TR (msec) |
TI (msec) |
FA (deg) |
Flipback (Present/Absent) |
Fat Sat (Type) |
ETL (Number) |
P-MRI (Reduction factor) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dual echo | T1_vibe_opp-in | 11 sec | 1.38/2.48 | 4.4 | 9 | |||||
| With a contrast agent | ||||||||||
| Dynamic | Vibe | 14 sec | 1.15 | 3.27 | 15 | |||||
| DWI | b=0,600,1000 | 3 mins | 82.1 | 20,000 | 90 | |||||
| T2WI | Ax T2 FS | 1 min | 74 | 2600 | 123 | |||||
| HBP | Vibe | 14 sec | 1.15 | 3.27 | 15 | |||||
| Imaging type | Breath hold (Present/Absent) |
NEX (Number of additions) |
k-space | In-plane resolution (mm) |
Slice thickness (mm) |
FA (deg) |
FOV (mm) |
Rectangular FOV (%) |
Phase direction (Number of steps) |
Lead direction (Number of matrices) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dual echo | present | 2.5 | 2.5 | |||||||
| With a contrast agent | ||||||||||
| Dynamic | present | 1.7 | 1.7 | |||||||
| DWI | absent | 5 | ||||||||
| T2WI | present | 5 | ||||||||
| HBP | present | 1.7 | 1.7 | |||||||
| Imaging type | Actual scan (%) |
Slice gap (mm) |
Number of slices | 3D partition (Number) |
3D actual scan (%) |
3D over sampling (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dual echo | 0 | 88 | ||||
| With a contrast agent | ||||||
| Dynamic | 0 | 128 | ||||
| DWI | 1 | 50 | ||||
| T2WI | 1 | 40 | ||||
| HBP | 0 | 128 | ||||
- *The case introduced is just one clinical case, so the results are not the same as for all cases.
- *Please refer to the Package Insert for the effects and indications, dosage and administration method, and warnings, contraindications, and other precautions with use.


