Usefulness of EOB-MRI for preoperative diagnosis of hepatic metastases after sigmoid colon cancer surgery.
Aichi Cancer Center Hospital
IVR Division, Dept. of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology
Drs. Shohei Chatani, Yoshitaka Inaba
DATE : 2021
Introduction

Patient’s background
Male; 60s; body weight: 54 kg; after sigmoid colon cancer surgery, but before hepatic metastasis resection.
Investigation objectives
Detailed tests for anemia were performed, and the diagnosis made was sigmoid colon cancer with associated synchronous hepatic metastases. The approach decided upon was resection of the sigmoid colon cancer first, followed 3 months later by resection of the hepatic metastases. At that time, contrast computed tomography (CT) suggested metastases at two loci; S5 and S7 of the liver. EOB-MRI was performed as a thorough examination before resection of the hepatic metastases.
Contrast agent used
Gadoxetate disodium(Gd-EOB-DTPA) injection, 0.1 mL/kg
Case explanation
Contrast CT showed a lesion in S5 of the liver (Fig. 1), and also a small-nodule-like, poor-contrast region below the S7 dome of the liver (Fig. 2), so metastasis was suspected. With respect to EOB-MRI of the S5 lesion, the arterial phase showed dark staining in the marginal region, and the hepatobiliary phase showed a signal lower than in the hepatic parenchyma, so metastasis was diagnosed (Fig. 3). In the case of the lesion below the S7 dome, in addition to the low signal in the hepatobiliary phase, with chemical shift imaging there was signal decrease in the opposed-phase in comparison with the in-phase (Figs. 4-6). On the basis of the characteristic position and the fat content, the lesion was judged to be hepatic pseudolipoma, and the diagnosis made was single hepatic metastasis. Hepatectomy was performed for the S5 lesion, and a pathological diagnosis of colonic cancer hepatic metastasis was made. The lesion below the S7 dome showed no marked changes in imaging over several years after surgery.
Imaging signs
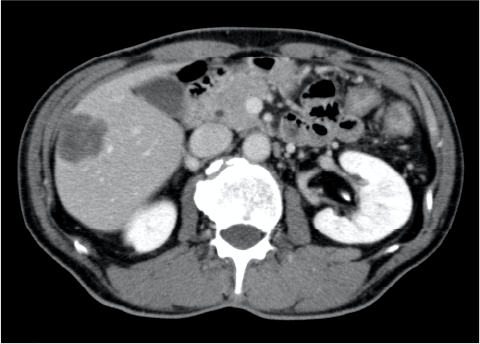
Fig. 1. S5 lesion, contrast CT equilibrium phase
A metastatic lesion with poor contrast enhancement was found in S5.
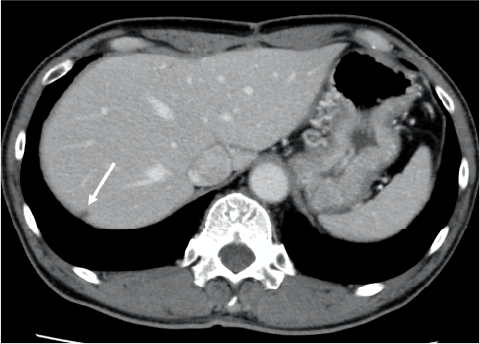
Fig. 2. Lesion below the S7 dome, contrast CT equilibrium phase
A small nodule (arrow) with poor contrast enhancement was found below the S7 dome, and metastasis was suspected.
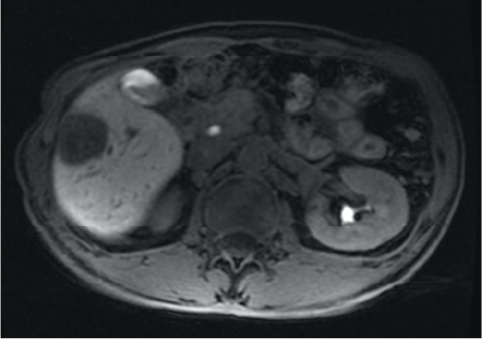
Fig. 3. S5 lesion,
EOB-MRI hepatobiliary phase
No uptake by the S5 lesion was found.
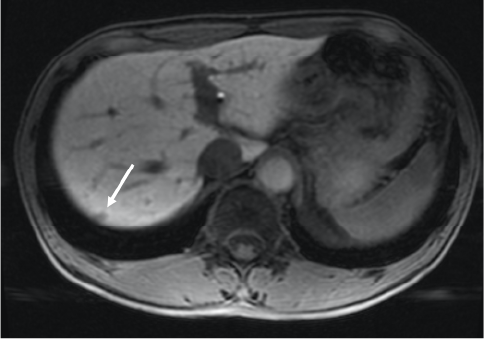
Fig. 4. Lesion below the S7 dome, EOB-MRI hepatobiliary phase
No uptake by the lesion (arrow) below the S7 dome was found.

Fig. 5. Lesion below the S7 dome, in-phase
The lesion (arrow) below the S7 dome had an iso-signal with the surrounding hepatic parenchyma.
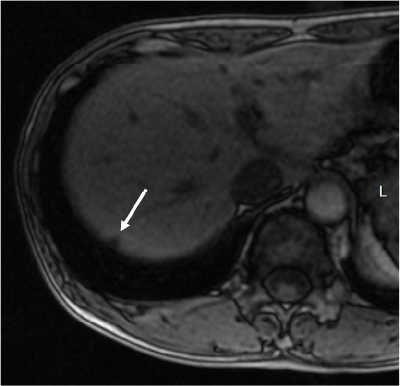
Fig. 6. Lesion below the S7 dome,
opposed-phase
The lesion (arrow) below the S7 dome showed a decreased signal, and microscopic fat content was suspected.
Photography protocol
| Imaging type |
Photography sequence |
Photography duration (s) |
TE (msec) |
TR (msec) |
TI (msec) |
FA (deg) |
Fat saturation (type) |
Holding breath (yes/no) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dual echo | ||||||||
| Contrast agent administration | ||||||||
| Dynamic | LAVA-FLEX | 18 | 1.7 | 4.0 | 0 | 12 | DIXON | Yes |
| DWI | DWI Prep | ー | 58.6 | 9000 | 110 | 90 | Chen-SAT | No |
| T2WI | SSFSE | 22 | 79.2 | 802.0 | 0 | 90 | ー | Yes |
| HBP | LAVA-FLEX | 18 | 1.7 | 4.0 | 0 | 12 | PIXON | Yes |
| Imaging type |
NEX (calculation number) |
In-plane resolution (mm) |
Slice thickness (mm) |
FOV (mm) |
Phase direction (step number) |
Read direction (matrix number) |
Slice Gap (mm) |
Slice number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dual echo | ||||||||
| Contrast agent administration | ||||||||
| Dynamic | 0.69 | 1.4×1.6 | 3.8 | 40 | 224 | 256 | 0 | 45 |
| DWI | 4 | 3.1×1.6 | 5 | 40 | 256 | 128 | 2 | 30 |
| T2WI | 0.57 | 1.1×1.9 | 5 | 40 | 192 | 320 | 2 | 30 |
| HBP | 0.69 | 1.4×1.6 | 3.8 | 40 | 224 | 256 | 0 | 45 |
Devices used and contrast conditions
| MRI device | SIGNA HDx6 3.0T |
|---|---|
| Automatic injection device | Sonic Shot GX |
| Work station | ー |
| Contrast conditions |
Dose (mL) | Administration rate (mL/s) | Photography timing | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gadoxetate disodium(Gd-EOB-DTPA) | 7.5 | 1.0 | Dynamic, three phases (after 40, 90 and 180 s), and 20 min | |
| Physiological saline solution for flushing | 40 | 1.0 |
Usefulness of Gadoxetate disodium(Gd-EOB-DTPA) contrast MRI with this patient
Hepatic metastasis resection for patients with colorectal cancer with associated hepatic metastases is a useful treatment option for improving long-term prognosis. It is preferable for the resection to remove the metastatic focus without residue, while conserving as much healthy hepatic tissue as possible. The hepatic pseudolipoma is considered to have been an epiploic appendix that became detached, moved freely, and later attached to the hepatic surface. Initially, it contained fat, but it underwent calcification with time. In some cases, even if fat detection is difficult with CT, it can be achieved with MRI, which is useful for definitive diagnosis. With the present case, analysis of the findings with each sequence, in addition to EOB-MRI contrast examination, enabled accurate preoperative diagnosis, and thus avoidance of unnecessary invasive treatment.
- *The case introduced is just one clinical case, so the results are not the same as for all cases.
- *Please refer to the Package Insert for the effects and indications, dosage and administration method, and warnings, contraindications, and other precautions with use.


