One case of EOB-MRI being useful for diagnosis of a hepatic inflammatory pseudotumor
Saitama Medical University Hospital
Dept. of Radiology
Drs. Yuki Hara, Eito Kozawa, and Atsushi Kondo
DATE : 2021
Introduction

Patient’s background
Male, 50s, body weight: 58 kg.
Investigation objectives
A high C-reactive protein level was shown during chemotherapy for acute myelogenous leukemia, so contrast computed tomography (CT) was performed to investigate the etiology in detail, and a hepatic mass was found. Initially, the lesion was suspected of being an abscess, but it showed no contraction after antibiotic administration, and contrast ultrasonography showed blood flow in the lesion region, so diagnosis as an abscess was ruled out. Therefore, EOB-MRI was performed for more detailed investigation.
Contrast agent used
Gadoxetate disodium(Gd-EOB-DTPA) injection, 0.1 mL/kg
Case explanation
As the lesion was suspected of being an inflammatory hepatic mass on the basis of various imaging results, a hepatic biopsy was performed, and a pathological diagnosis consistent with an inflammatory pseudotumor was made. Antibiotic administration and leukemia treatment were continued, and follow-up CT showed the hepatic mass to decrease in size and finally disappear.
Imaging signs
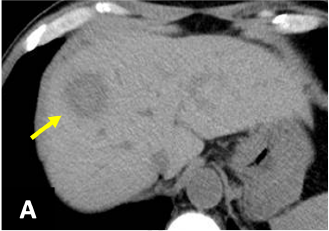
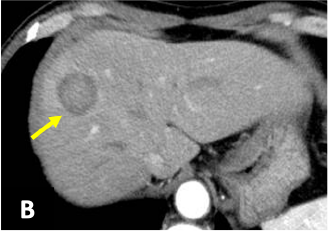
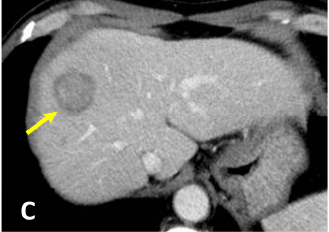
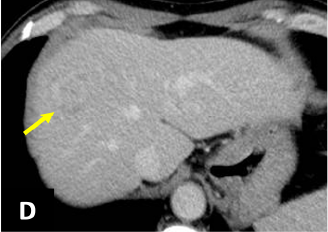
Fig. 1. Dynamic CT (A: simple; B: arterial phase;
C: portal phase; D: delayed phase)
A mass 25 mm in diameter, with somewhat indistinct delineation, was found in S8 of the liver (→).
The margin showed delayed dark staining in a ring shape, and in the arterial phase there was faint contrast in the interior of the lesion.
CT showed the lesion to have expanded in comparison with 11 days previously (not shown), indicating short-term changes in size.
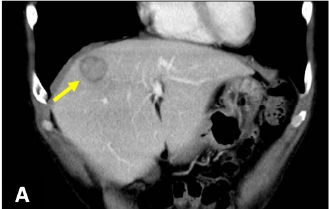
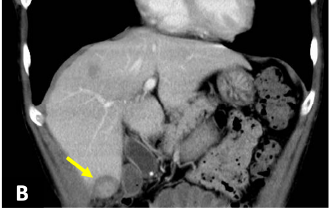
Fig. 2. CT coronal section (portal phase)
A similar lesion to that in S8 (A: →) was found in the lower part of S5/6 (B: →).
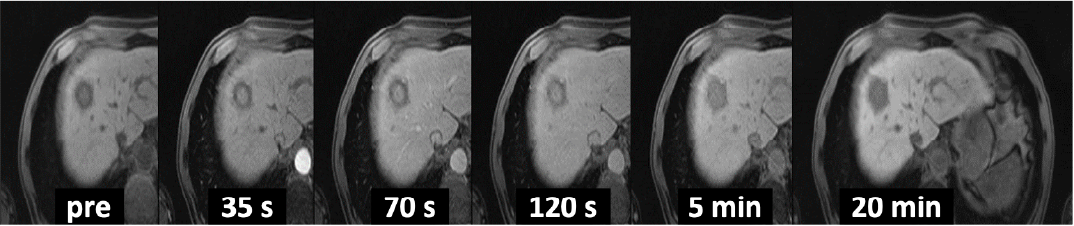
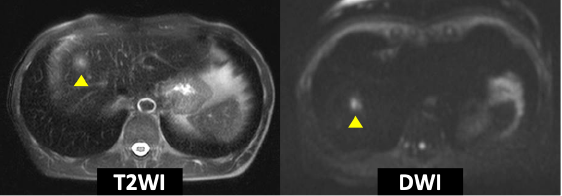
Fig. 3. EOB-MRI
In the dynamic study, the marginal region showed a ring-shaped, low-signal area, and was suspected, taking the CT findings into consideration, of being a fibrotic entity. In T2WI and DWI, the interior showed a faint high signal (▲), but it showed delayed dark staining, so the signs were different from those expected with an abscess. In the hepatobiliary phase after 20 minutes, the entire mass showed a low signal.
Photography protocol
| Imaging type | Photography sequence |
Photography duration |
TE (msec) |
TR (msec) |
FA (deg) |
Fat saturation (type) |
ETL number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dual echo | FLASH | 18 s | 1.23 2.46 |
170 | 70 | ー | ー |
| Contrast agent administration | |||||||
| Dynamic | VIBE | 15 s | 1.2 | 3.5 | 10 | Q-fat sat | ー |
| DWI | EPI | 3 min 17 s | 65 | 6100 | 90 | SPAIR | ー |
| T2WI | TSE | 5 min | 90 | 3000 | 120 | SPAIR | 14 |
| HBP | VIBE | 15 s | 1.2 | 3.5 | 10 | Q-fat sat | ー |
| Imaging type | P-MRI (Reduction Factor) |
Holding breath (yes/no) |
k-space | In-plane resolution (mm) |
Slice thickness | FOV (mm) |
Rectangular FOV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dual echo | 2 | + | sequential | 0.7×0.7 | 6 | 350 | 75 |
| Contrast agent administration | |||||||
| Dynamic | 3 | + | sequential | 1.4×1.4 | 3.5 | 350 | 87.5 |
| DWI | 2 | - | sequential | 2.3×2.3 | 6 | 360 | 81.3 |
| T2WI | 3 | - | *Note: | 1.1×1.1 | 6 | 350 | 100 |
| HBP | 3 | + | sequential | 1.4×1.4 | 3.5 | 350 | 87.5 |
| Imaging type | Phase direction (step number) |
Read direction (matrix number) |
Actual scan (%) |
Slice Gap (mm) |
Slice number | 3D actual scan (%) |
3D over sampling(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dual echo | 173 | 256 | ー | 1.8 | 24 | ー | ー |
| Contrast agent administration | |||||||
| Dynamic | 179 | 256 | 100 | ー | 60 | 56 | 20 |
| DWI | 104 | 160 | ー | 0 | 35 | ー | ー |
| T2WI | ー | 320 | ー | 0 | 38 | ー | ー |
| HBP | 179 | 256 | 100 | ー | 60 | 56 | 20 |
Devices used and contrast conditions
| MRI device | MAGNETOM Skyra |
|---|---|
| Automatic injection device | Sonic Shot GX |
| Work station | ー |
| Contrast conditions |
Dose (mL) | Administration rate (mL/s) | Photography timing | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gadoxetate disodium(Gd-EOB-DTPA) | 0.1mL/kg | 1 | Test bolus | |
| Physiological saline solution for flushing | ー | 2 |
- *Note:T2WI was performed with diaphragmatic respiration synchronization (prospective acquisition correction) and the blade method.
DWI was performed with free-breathing.
Usefulness of Gadoxetate disodium(Gd-EOB-DTPA) contrast MRI with this patient
No reviews covering the imaging signs with hepatic inflammatory pseudotumors have been published, and, as hepatic inflammatory pseudotumors take various forms, it is often difficult to distinguish them from malignant tumors and/or abscesses. With the present patient, delayed dark staining was found, reflecting the high degree of fibrosis of the lesion, and, together with the time-course of size changes, this suggested the possibility of the lesion being an inflammatory mass. Further investigations were then performed until the final diagnosis was made.
- *The case introduced is just one clinical case, so the results are not the same as for all cases.
- *Please refer to the Package Insert for the effects and indications, dosage and administration method, and warnings, contraindications, and other precautions with use.


