Simple nodular hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): Pathology and comparison
Tokyo Women's Medical University
Dr. Shun-ichi Ariizumi
DATE : 2009
Simple nodular HCC with parts of the interior separated by the septum having different properties

Patient’s background and objectives of MRI
Male, 57 years old.
Primary complaint: None
History of current condition: Chronic hepatitis C was diagnosed at a different hospital in 1997.
Interferon therapy was then administered.
In 2008, PIVKA-II increased, and HCC was diagnosed on the basis of computed tomography (CT), so the patient was referred to the author’s hospital.
Blood chemistry test results: Leukocytes: 3200 /μL; hemoglobin: 12 g/dL; platelets: 4.6 × 104 /μL; AST: 94 IU/L; ALT: 69 IU/L; total bilirubin: 0.7 mg/dL; albumin: 3.2 g/dL; prothrombin time: 85%; ICGR15: 25%; Child-Pugh class: A; HBs antigen: negative; HBe antigen: negative; HCV antibody: positive; AFP: 922 ng/mL; PIVKA-II: 3149 mAU/mL.
Abdominal CT findings
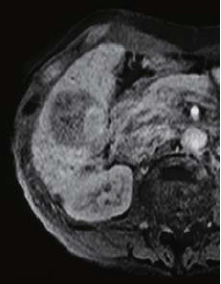
Simple CT showed a tumor 4.5 cm in diameter in the posterior segment.In the contrast CT arterial phase, dark staining was seen in the left third of the tumor interior, but contrast was poor in the right two thirds.
In the equilibrium phase, overall absorption decreased, and an entire-circumference corona was found to surround the tumor.
EOB-MRI findings
The right two thirds of the tumor interior showed a low signal in T1-weighted imaging (in phase), and a high signal in T2-weighted imaging. The left third of the tumor interior showed a high signal in T1-weighted imaging (in phase), and a low signal in T2-weighted imaging (no photographs are shown). The right two thirds of the tumor interior showed a pre-contrast iso-signal, and, in the dynamic study, a heterogeneous high signal 20 s after administration, and a low signal 60 and 120 s after administration. The left third of the tumor interior showed a pre-contrast high signal, and, in the dynamic study, a more intensely high signal from 20 s after administration, with the tumor being hypervascular. In the hepatobiliary phase, the right two thirds of the tumor interior showed a low signal, and the left third showed a higher signal than the surrounding liver. No projections or irregularities were found in the surrounding liver.
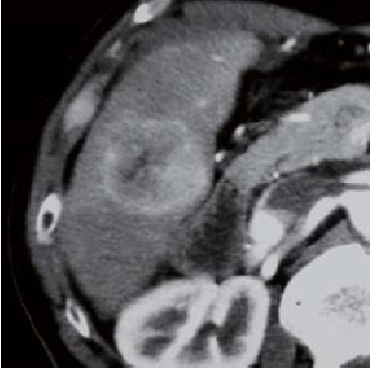
Contrast CT arterial phase
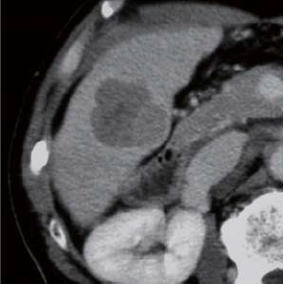
Contrast CT equilibrium phase
Abdominal CT findings
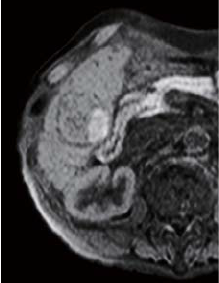
Pre-contrast
EOB-MRI findings
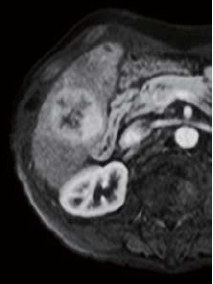
20 s after administration
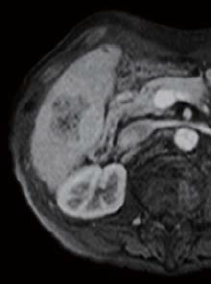
60 s after administration
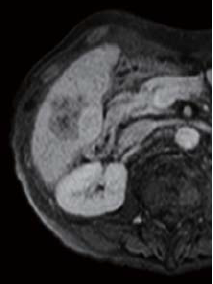
120 s after administration
Hepatobiliary phase
EOB-MRI findings
Surgery
Excision of S6 was performed.
Macroscopic observation of resection samples
The tumor was a simple nodular type, with a capsule, and the left third of the tumor interior, separated by a septum, was a pale green color, indicating bile production. The right two thirds of the tumor interior was white, and contained scattered hemorrhagic foci.
Histopathology findings
(i) Two nodes were fused, and the node on the right side of the photograph appeared green in macroscopic observation. (ii) The two nodes, to the right and left of the central septum, were HCC with different histological images. The left node was moderately differentiated, and the right node was highly differentiated.
(iii) “b” shows a region that is highly differentiated, with mild cellular atypia, a relatively fine cord, and a pseudoglandular tube. The brightness and fine granular appearance of the cells suggests cholestasis.
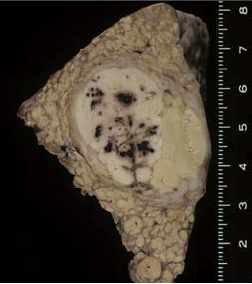
Findings with macroscopic
observation
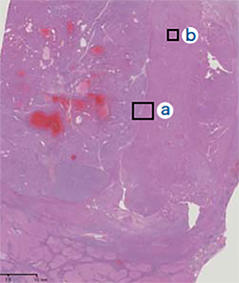
(i)
Histopathology findings
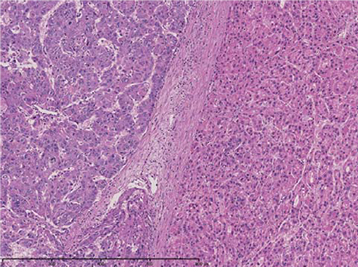
(ii) Magnification of “a”
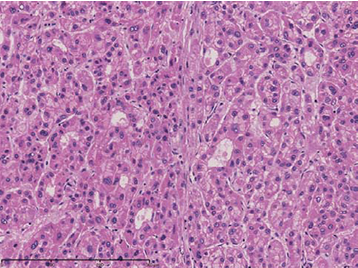
(iii) Magnification of “b”
Histopathology findings
- *The case introduced is just one clinical case, so the results are not the same as for all cases.
- *Please refer to the Package Insert for the effects and indications, dosage and administration method, and warnings, contraindications, and other precautions with use.


